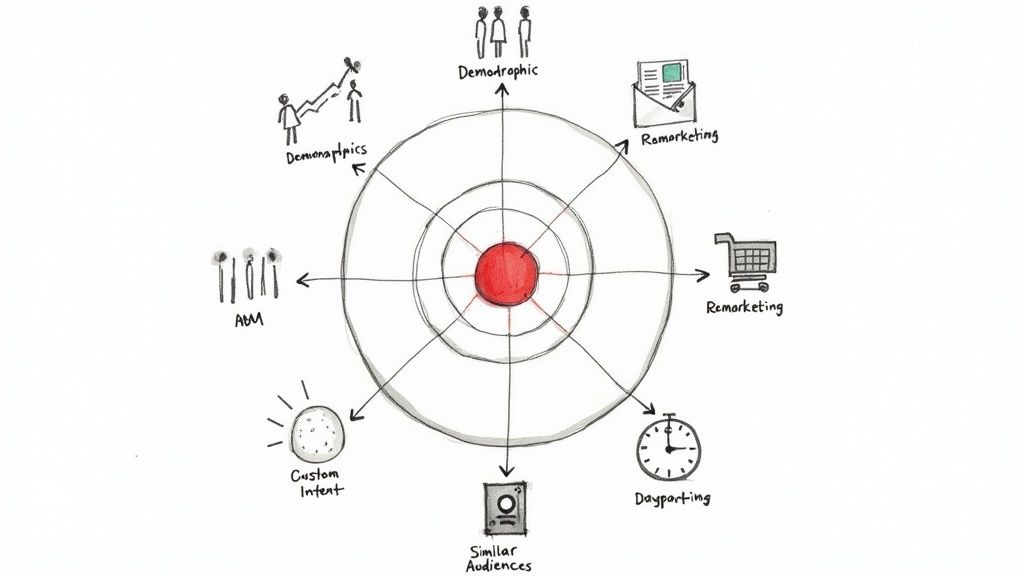
In the highly competitive arena of Google Ads, relying solely on keyword bids is a surefire way to fall behind. Winning today means reaching the exact right person, at the precise right moment, with a message that resonates. This level of precision requires a sophisticated approach to targeting strategies marketing professionals use to transform ad spend into tangible results. Simply put, if you aren't actively layering advanced audience targeting, you are leaving money on the table.
This article moves beyond the basics and dives deep into nine powerful audience targeting methods you can implement directly within the Google Ads ecosystem. We will unpack the "how-to" for each strategy, providing actionable steps and real-world examples to guide your setup. You will learn how to go from broad-stroke campaigns to hyper-focused initiatives that speak directly to specific user segments.
Forget generic advice. Prepare to explore the nuances of user intent, behavior, and context within Google's powerful platform. We'll cover everything from precise demographic and geographic segmentation to advanced techniques like behavioral targeting and account-based marketing (ABM) using Google's tools. By the end of this guide, you will have a clear roadmap for combining these strategies, creating a formidable campaign structure that maximizes your return on ad spend (ROAS) and drives significant growth. Let's get started.
1. Demographic Segmentation
Demographic segmentation is one of the most foundational and widely used targeting strategies within the Google Ads platform. It involves dividing your audience into distinct groups based on observable, person-based attributes like age, gender, income level, education, and parental status. This method provides a clear, data-driven starting point for understanding who your customers are and how to reach them on Google's network.
Because these characteristics are often linked to purchasing habits and needs, demographic targeting allows you to tailor your ad copy, creative, and bids to resonate with specific segments. For example, a high-end financial services firm would target users in the top household income tiers on Display and YouTube, while a toy company would focus on the "Parents" audience segment.
How to Use Demographics in Google Ads
Google Ads makes it easy to implement demographic targeting. When setting up a Search, Performance Max, Display, Video, or Discovery campaign, you can navigate to the "Audiences" section and select your desired demographic groups.
- Age: Target specific age ranges (e.g., 18-24, 25-34).
- Gender: Choose to show ads to Male, Female, or Unknown.
- Parental Status: Target Parents, Not a parent, or Unknown.
- Household Income: Focus on specific income brackets (e.g., Top 10%, 11-20%), although this is only available in select countries.
Pro Tip: Don't just target; also exclude. If you sell luxury retirement homes, you can exclude younger age groups and lower income brackets to prevent budget waste and focus your ad spend on the most qualified audience. This is a crucial optimization tactic.
When to Use This Strategy
Demographic segmentation is an excellent starting point for nearly any Google Ads campaign, as it helps establish a baseline audience. It's particularly effective when your product or service naturally appeals to a specific group. A company selling life insurance, for instance, would benefit greatly by targeting users based on age and parental status.
However, relying solely on demographics can be limiting. The most powerful Google Ads strategies layer demographic data with other targeting methods, like behavioral or in-market audiences, to build a more nuanced and accurate picture of the ideal customer. This layered approach ensures your message reaches not just the right type of person, but the right person at the right time.
2. Psychographic Segmentation
While demographics tell you who your audience is, psychographic segmentation explains why they buy. This powerful Google Ads targeting strategy groups consumers based on their psychological attributes, including their lifestyle, values, attitudes, and interests. It moves beyond basic data to uncover the motivations driving purchasing decisions, allowing for deeply resonant ad campaigns.
This approach is about connecting with people on an emotional and personal level. For example, a brand like Patagonia doesn't just target "people who hike"; it targets individuals who value environmental sustainability and adventure. On Google Ads, this translates to layering demographic data with specific Affinity Audiences and custom segments that reflect these values.
How to Use Psychographics in Google Ads
While Google Ads doesn't have a direct "psychographics" filter, you can effectively reach these segments by combining different audience signals that reflect psychological traits.
- Affinity Audiences: Target users based on their long-term interests and habits (e.g., "Thrill Seekers," "Health & Fitness Buffs," "Green Living Enthusiasts"). Google builds these profiles based on browsing history and content consumption.
- In-Market Audiences: Reach users actively researching products or services, which often reflects their immediate needs and values (e.g., "Eco-Friendly Vehicles," "Home Gym Equipment").
- Custom Segments: Build your own audience by entering keywords, URLs, and apps that your ideal customer profile would engage with. To target environmentally conscious consumers, you could input keywords like "sustainable fashion" and URLs of popular eco-friendly blogs.
Pro Tip: Use Google Analytics 4's audience builder to discover psychographic insights. Analyze the "Interests" reports to see which Affinity and In-Market segments your highest-converting users belong to, then use those exact segments in your Google Ads campaigns.
When to Use This Strategy
Psychographic segmentation is ideal when you want to build a strong brand identity and foster a loyal community around shared values. It is one of the most effective targeting strategies marketing teams can use within Google Ads to differentiate from competitors who may only be focusing on demographics. This strategy works exceptionally well for brands in competitive markets where emotional connection, not just product features, drives sales.
By layering psychographic insights onto your demographic data, you create a multi-dimensional view of your customer. This allows you to craft ad copy and creative that speaks directly to their core beliefs and motivations, transforming a simple ad into a meaningful brand interaction.
3. Geographic Segmentation
Geographic segmentation within Google Ads involves dividing your market based on location, such as country, region, city, or even postal code. This foundational targeting strategy operates on the simple premise that a consumer's needs, preferences, and purchasing power can change drastically depending on where they live, influenced by factors like culture, climate, and local economy.
Because location directly impacts lifestyle, geographic targeting allows you to create highly relevant and localized campaigns. For example, a home improvement retailer would use location targeting to promote hurricane-resistant building materials in coastal Florida, while advertising snow blowers in the Northeast during winter. This ensures ad spend is concentrated only in relevant areas.
How to Use Geographics in Google Ads
Google Ads offers powerful and granular location targeting options directly within the campaign settings, allowing you to zero in on specific areas or exclude irrelevant ones.
- Location Targeting: Navigate to your campaign "Settings" and then "Locations." Here you can target entire countries, states/provinces, cities, and even specific postal codes.
- Radius Targeting: Use this to target a specific radius (in miles or kilometers) around a business address. This is ideal for local businesses running campaigns to drive foot traffic or local service calls.
- Location Groups: Target groups of locations, such as "Places of interest" (e.g., airports, universities) or tiered income areas within a country.
Pro Tip: Go beyond just targeting locations. Use the "Presence or interest" setting. Select "Presence: People in or regularly in your targeted locations" to avoid showing ads to users who are merely interested in your location but don't live there. This is a critical setting for local service providers to avoid wasted budget.
When to Use This Strategy
Geographic segmentation is essential for any business with a physical presence or one that serves specific service areas. It's also critical for e-commerce brands looking to optimize shipping costs or tailor promotions to regional holidays and events. This strategy is a cornerstone of effective targeting strategies in marketing.
However, its true power in Google Ads is unlocked when layered with other targeting methods. Combining geographic data with behavioral or demographic insights allows you to reach not just people in the right city, but the right type of person in that city who is actively searching for what you offer.
4. Behavioral Segmentation
Behavioral segmentation moves beyond who your audience is and focuses on what they do online. This powerful Google Ads strategy involves grouping consumers based on their actions, such as their search history, website visits, video views, and app usage. Google's vast ecosystem provides a rich source of behavioral data, giving advertisers deep insights into customer intent and readiness to buy.
This method allows marketers to create highly relevant and timely campaigns. For example, serving a remarketing ad for a specific product to someone who added it to their cart but didn't check out is a classic and effective use of behavioral targeting. It leverages past user actions to predict future interest.
How to Use Behavioral Targeting in Google Ads
Google Ads offers several ways to leverage user behavior, primarily through audience segments built from your website and app data (first-party data) or from Google's network data (Google data). You can find these options under "Audience manager" and apply them to your campaigns.
- Your Data Segments (Remarketing): Target users who have visited your site, added items to a cart, or completed a specific action. This is the most powerful form of behavioral targeting.
- In-Market Segments: Reach users whose online behavior indicates they are actively researching and considering products or services like yours. Google identifies these behaviors across its network.
- Affinity Audiences: Target users based on their long-term interests and habits, as demonstrated by their online browsing and search behavior.
- Custom Segments: Build audiences based on specific search terms users have typed into Google, websites they've visited, or apps they use to pinpoint high-intent users.
Pro Tip: Use behavioral triggers for automated sequences. For example, create a specific Display or YouTube remarketing campaign targeting users who abandoned their shopping cart, offering them a small discount to encourage them to complete the purchase. This is a classic yet highly effective behavioral tactic.
When to Use This Strategy
Behavioral segmentation is essential for any business focused on personalization and optimizing the customer journey within the Google Ads ecosystem. It is incredibly effective for e-commerce, SaaS, and lead generation. By understanding what users do, you can tailor messaging to guide them through the funnel, from initial awareness to loyal advocacy.
Layering behavioral data with other targeting strategies marketing methods, like demographics, creates a robust and highly accurate profile of your ideal customer. To truly master this, you need to understand how these audiences drive conversions. For a complete overview of turning clicks into customers, explore our Google Ads lead generation guide.
5. Benefit Segmentation
Benefit segmentation is a strategic approach that groups consumers based on the specific value or benefits they seek from a product. Instead of focusing on who the customers are, this approach prioritizes why they are searching on Google. It recognizes that different people can search for the same product for entirely different reasons, such as convenience, performance, social status, or cost savings.
This strategy goes beyond surface-level attributes to uncover the core motivations driving searches and clicks. By understanding these motivations, you can craft highly specific ad copy and landing pages that speak directly to what each segment values most. For example, a mattress company might target one group with ads about "back pain relief" and another with ads about "luxury comfort," all for the same product.
How to Use Benefit Segmentation in Google Ads
While Google Ads doesn't have a direct "benefit-seeking" audience category, you can apply this strategy by aligning your ad components with the benefits your audience desires. This involves creating separate campaigns or ad groups for each benefit segment.
- Keyword Targeting: Create ad groups with keywords that reflect specific benefits. For example, "running shoes for marathon training" (performance benefit) vs. "comfortable daily walking shoes" (comfort benefit).
- Ad Copy: Write headlines and descriptions that explicitly mention the benefit. One ad could read, "Achieve Your Personal Best," while another for a different segment says, "All-Day Comfort, Guaranteed." This directly addresses the searcher's intent.
- Landing Pages: Direct traffic to unique landing pages that expand on the promised benefit, reinforcing the message and improving Quality Score and conversion rates.
Pro Tip: Use Custom Segments to build audiences based on benefit-related search terms. Create an audience of users who have searched on Google for "eco-friendly cleaning products" or "hypoallergenic laundry detergent" to target people actively seeking those specific benefits in Display or Video campaigns.
When to Use This Strategy
Benefit segmentation is highly effective when your product serves multiple purposes or solves different problems for various user types. It works exceptionally well in mature markets where consumers are making choices based on specific needs rather than general product categories. For this to work, a deep understanding of your audience is crucial. A key part of the process involves identifying customer pain points to ensure your messaging aligns with their real-world challenges.
By focusing on the "why" behind the search, you create more resonant and persuasive advertising. Layering benefit-based messaging on top of demographic or behavioral targeting creates a comprehensive approach, ensuring your ads reach not just the right people, but also with the right message that truly motivates them to act.
6. Occasion-Based Segmentation
Occasion-based segmentation is a powerful Google Ads strategy that targets consumers based on specific situations, events, or times when they are most likely to need a product or service. This approach recognizes that a person's needs and purchasing intent can change dramatically depending on the context, such as a holiday, a personal milestone, or even the time of day.
This targeting strategy moves beyond who the customer is and focuses on when they are searching. For example, a flower delivery service doesn't just target people who like flowers; it targets users searching for "same-day flower delivery" in the days leading up to Valentine's Day or Mother's Day. This is about capturing intent at the moment of highest relevance.
How to Use Occasion-Based Targeting in Google Ads
While Google Ads doesn't have a direct "Occasion" setting, you can creatively use its features to achieve this. The key is to align your campaign's keywords, ad copy, and scheduling with specific events.
- Keyword Targeting: Bid on occasion-specific keywords like "last minute mother's day gifts" or "black friday laptop deals."
- Ad Scheduling: Use dayparting to run ads at peak times. A food delivery service could increase bids during lunch and dinner hours, or a transportation app could boost visibility on a Friday night.
- Ad Customizers: Use countdown timers in your ad copy to create urgency for events like sales or holidays (e.g., "Sale Ends In {=COUNTDOWN("2024/11/29 09:00:00")}").
- In-Market Audiences: Target users actively researching for event-related products, such as "Holiday & Seasonal Shopping," which is a predefined Google audience segment.
Pro Tip: Build separate campaigns for major occasions like Black Friday or Valentine's Day. This allows you to set dedicated budgets, create highly specific ad copy and landing pages, and track the performance of each event independently without disrupting your evergreen campaigns.
When to Use This Strategy
Occasion-based targeting is essential for businesses whose products are tied to specific seasons, holidays, life events, or recurring needs. It is one of the most effective targeting strategies marketing can employ for driving timely, high-intent conversions within Google Ads. Florists, gift shops, event planners, and seasonal retailers rely heavily on this approach.
However, its use isn't limited to seasonal businesses. A B2B software company could use it to target businesses searching for "end of year budget software" at the end of a financial quarter. By understanding the "when," you can connect with your audience at the precise moment they are ready to buy.
7. Micro-Targeting
Micro-targeting is a highly sophisticated strategy that leverages Google's vast data signals to identify and engage extremely narrow audience segments with personalized messages. Instead of targeting broad categories like "sports fans," micro-targeting drills down into hyper-specific niches, such as "35-40 year old urban males who have recently searched for 'buy marathon running shoes' and visited nutrition blogs."
This approach combines multiple data points, including demographics, search history, online behaviors, and purchase signals, to create precise targeting parameters. The goal is to make the marketing message feel as if it was created specifically for the individual receiving it, dramatically increasing its relevance and potential for conversion within the Google Ads platform.
How to Use Micro-Targeting in Google Ads
The principles of micro-targeting are directly applicable within the Google Ads ecosystem, primarily through the creation of custom segments and audience layering.
- Custom Segments (Interests/Behaviors): Go to Audience Manager and create a new custom segment. Combine interests, specific URLs (e.g., competitor websites), and app usage to define a micro-audience.
- Custom Segments (Search Terms): Create a segment of "People who searched for any of these terms on Google." Enter a list of 10-15 highly specific, long-tail keywords that your ideal customer would use. For example, instead of "CRM software," use "CRM for small law firms" or "best CRM with Outlook integration."
- Layering Audiences: Apply a custom segment on top of a demographic or in-market audience to further refine your targeting. For instance, target an in-market audience for "Business Software" but only show ads to users who also match your custom segment of people who searched for specific competitor names.
Pro Tip: When building micro-segments, think about intent signals. Combining searches for a problem (e.g., "how to automate client onboarding") with visits to solution-oriented websites (by adding their URLs to a custom segment) creates a powerful, high-intent micro-audience ready to convert.
When to Use This Strategy
Micro-targeting is ideal for high-value products or services with a long sales cycle, or for advertisers operating in highly competitive niches where broad targeting is too expensive. It allows you to focus your budget exclusively on users with the highest probability of converting.
However, this strategy requires a deep understanding of your customer and their online journey. It's crucial to balance personalization with privacy, ensuring all targeting practices comply with regulations like GDPR and CCPA. When executed correctly, micro-targeting is one of the most powerful targeting strategies marketing can offer, delivering exceptional ROI by speaking directly to the few who matter most.
8. Generational Marketing
Generational marketing is a strategic approach that segments audiences based on the generation they were born into, such as Baby Boomers, Generation X, Millennials, and Gen Z. This method operates on the principle that shared historical events and cultural trends create distinct values, communication styles, and purchasing behaviors for each cohort, which directly impacts how they use Google and YouTube.
This strategy allows marketers to craft messaging and select channels that align with the unique preferences of each group. For example, a campaign targeting Gen Z might leverage authentic, short-form video content on YouTube Shorts, while a campaign for Baby Boomers could find more success with detailed product information in Search ads or on Display.
How to Use Generational Insights in Google Ads
While Google Ads doesn't have a direct "Generation" targeting option, you can effectively reach these cohorts by combining demographic data with other signals that reflect generational preferences.
- Age Ranges: Use age targeting as your foundation. For example, target ages 18-27 for Gen Z or 59-77 for Baby Boomers.
- Affinity & In-Market Audiences: Layer age targeting with relevant interests. To reach Millennials, you might add affinity audiences like "Foodies" or "Technophiles," which are heavily populated by this demographic.
- Keywords & Placements: Target keywords and YouTube placements that are popular with specific generations. A Gen Z campaign might focus on influencer collaboration channels and search terms like "dupes for [product]," while a Gen X campaign could use keywords related to financial planning or home improvement.
Pro Tip: Look beyond simple age brackets and consider life stage audiences. Targeting "new homeowners" or "recent college graduates" often captures a specific generational mindset and need, making your ads more contextually relevant and effective.
When to Use This Strategy
Generational marketing is most effective when your product, service, or brand ethos strongly aligns with the core values of a particular generation. A company selling sustainable goods would naturally resonate with the values of many Millennials and Gen Z consumers, making this an ideal targeting strategy. Similarly, services related to retirement planning are a perfect fit for Baby Boomers.
However, be cautious of stereotypes. The best generational targeting strategies marketing plans use broad generational insights as a starting point, then refine them with behavioral and psychographic data within Google Ads. This ensures your campaigns connect with real people and their individual needs, not just a generalized demographic label.
9. Account-Based Marketing (ABM)
Account-Based Marketing (ABM) flips the traditional lead generation funnel on its head. Instead of casting a wide net to capture many leads, ABM is a highly focused B2B strategy that treats individual high-value accounts as their own unique markets. Within the Google Ads ecosystem, this means creating hyper-personalized campaigns aimed at specific companies and their decision-makers.
This laser-focused approach is ideal for businesses with long sales cycles and high-value deals, such as enterprise SaaS companies. For example, a firm like Salesforce might create a bespoke Google Ads campaign targeting employees at a specific Fortune 500 company, addressing its unique pain points and decision-makers directly, rather than using a broad, generalized message.
How to Use ABM in Google Ads
While often associated with platforms like LinkedIn, Google Ads can be a powerful tool for ABM when used strategically. The key is to leverage its precise targeting capabilities to reach decision-makers at your target accounts.
- Customer Match: This is the cornerstone of ABM in Google Ads. Upload a list of business emails from key contacts at your target companies. You can use this list to target them across Search, Display, YouTube, and Gmail.
- Custom Segments: Create a custom audience based on URLs of your target companies. Apply this to a Display or Video campaign to serve ads specifically to people who browse those corporate websites.
- Layered In-Market Audiences: Combine in-market audiences (e.g., "Business Financial Services") with location targeting set to the specific office locations of your target accounts to narrow your reach.
- Keyword Targeting: Focus on long-tail, high-intent keywords that C-level executives at your target companies would search for, such as "enterprise CRM solutions" or "cloud migration strategy for finance."
Pro Tip: Create a dedicated Remarketing List for users who visit a specific landing page designed for a target account. You can build these audiences by adding a unique URL parameter to the links you send them and creating an audience rule based on that parameter.
When to Use This Strategy
ABM is not for every business. It's most effective for B2B companies that sell high-contract-value products or services to a limited number of identifiable companies. If your ideal customer profile is "any small business," ABM is likely too resource-intensive.
However, if your growth depends on landing a handful of large, strategic accounts each year, ABM is one of the most powerful targeting strategies in marketing. It ensures alignment between your sales and marketing teams, reduces wasted ad spend, and significantly improves the chances of closing deals with your most important prospects.
Targeting Strategies Comparison Matrix
| Segmentation Type | Implementation Complexity 🔄 | Resource Requirements ⚡ | Expected Outcomes 📊 | Ideal Use Cases 💡 | Key Advantages ⭐ |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Demographic Segmentation | Low 🔄 | Low ⚡ | Broad market reach, measurable segments 📊 | Mass marketing, traditional media, quick segmentation | Simple, cost-effective, widely applicable ⭐ |
| Psychographic Segmentation | High 🔄 | High ⚡ | Deep consumer insights, emotional connection 📊 | Brands seeking differentiation and loyalty | Predictive, emotionally engaging ⭐ |
| Geographic Segmentation | Low 🔄 | Low ⚡ | Localized marketing, regional relevance 📊 | Local businesses, climate or culture-based targeting | Easy to implement, cost-effective for local focus ⭐ |
| Behavioral Segmentation | High 🔄 | High ⚡ | Personalized marketing, predictive 📊 | Data-driven marketing, retention, loyalty programs | Data-driven, highly predictive ⭐ |
| Benefit Segmentation | Medium 🔄 | Medium ⚡ | Targeted messages based on needs 📊 | Product development, value-focused campaigns | Addresses core customer benefits ⭐ |
| Occasion-Based Segmentation | Medium 🔄 | Medium ⚡ | Timely, relevant messaging 📊 | Seasonal promotions, event marketing | Creates urgency, seasonal relevance ⭐ |
| Micro-Targeting | Very High 🔄 | Very High ⚡ | Extremely precise targeting, high conversion 📊 | Advanced digital campaigns, personalized ads | Precision, efficient ad spend, personalization ⭐ |
| Generational Marketing | Medium 🔄 | Medium ⚡ | Cohort-based preferences, cultural relevance 📊 | Age-cohort targeting, generational campaigns | Clear segments, predictable media use ⭐ |
| Account-Based Marketing (ABM) | Very High 🔄 | Very High ⚡ | High ROI, personalized B2B campaigns 📊 | B2B enterprise targeting, high-value accounts | Strong alignment between sales & marketing ⭐ |
Layering Your Strategies for Unbeatable Results
Navigating the world of targeting strategies marketing can feel like trying to find a single person in a crowded stadium. Shouting into the void is expensive and ineffective. As we've explored, the solution isn't to shout louder, but to speak more directly to the right people. From the foundational logic of demographic and geographic segmentation to the nuanced precision of psychographic, behavioral, and even account-based marketing, you now have a comprehensive toolkit for building highly effective Google Ads campaigns.
The journey doesn't end with mastering a single strategy. The real art and science of Google Ads mastery lies in the intelligent combination of these approaches. Each strategy we've covered is a powerful tool on its own, but when layered together, they create a synergistic effect that amplifies your results, sharpens your relevance, and dramatically improves your return on ad spend (ROAS).
From Broad Strokes to Surgical Precision
Think of your targeting layers like filters, each one refining your audience until you are left with only the most qualified and high-intent prospects. A broad demographic target is your first, widest filter. Layering on an In-Market or Affinity audience adds a second, more refined filter based on active interest. Further segmenting with a Remarketing List for Search Ads (RLSA) or a Customer Match list acts as your finest filter, ensuring your message reaches those with a proven connection to your brand.
This multi-layered approach is where good campaigns become great. For instance, a campaign could start by targeting:
- Layer 1 (Foundation): Women, ages 25-44, located in major metropolitan areas (Demographic + Geographic).
- Layer 2 (Intent): Who are also in the "Home & Garden" In-Market segment (Behavioral).
- Layer 3 (Connection): And have previously visited your "outdoor furniture" category page but did not convert (Remarketing).
This combination transforms a generic ad into a hyper-relevant message delivered at the perfect moment. Each layer validates the next, drastically increasing the probability of a conversion and ensuring your budget is spent with maximum efficiency. To truly excel in layering your marketing efforts, it’s crucial to start with the foundational step of understanding your audience; learn more about building a robust customer segmentation strategy to create a solid base for all your campaigns.
Your Actionable Path Forward
Mastering these advanced targeting strategies marketing is not a one-time setup; it's an ongoing process of refinement. The Google Ads ecosystem is dynamic, and your ability to adapt will define your success. Start by reviewing your current campaigns. Identify one or two where you can apply a new layer of targeting. Monitor the performance closely in the 'Audiences' tab, paying attention to metrics like click-through rate (CTR), conversion rate, and cost-per-acquisition (CPA).
Don't be afraid to experiment. Test different combinations of audiences. Use the 'Observations' setting to gather data without restricting reach, then switch to 'Targeting' once you've identified a winning combination. By embracing this iterative process of testing, learning, and refining, you move beyond simply managing campaigns. You begin to architect a predictable, scalable, and highly profitable growth engine for your business or your clients.
Ready to supercharge your lead generation and ensure your meticulously targeted traffic converts? Pushmylead provides a suite of powerful tools designed to capture, qualify, and route leads from your Google Ads campaigns with unmatched efficiency. Stop letting valuable prospects slip through the cracks and connect your targeting efforts directly to your sales pipeline with Pushmylead.